Treatment For Acne Fulminans
2 min read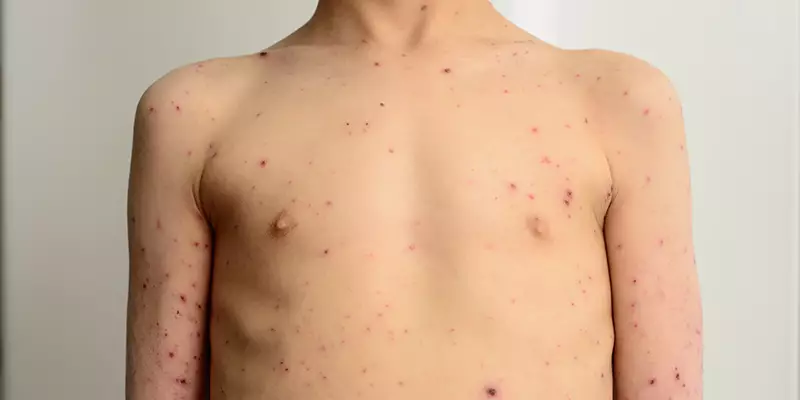
Treatment for acne fulminans usually consists of corticosteroid therapy or isotretinoin. Neither of these drugs should be used as first-line therapy nor as monotherapy. Because of its rarity and understudied nature, doctors are often unaware of the symptoms of this disease. It is distinguished from typical acne by its explosive worsening of lesions, as well as by its occurrence in younger patients and in those without facial granulation tissue.
Acne fulminans is a rare disease caused by an underlying immune system disorder. Although its incidence is on the decline, acne fulminans is still a very painful and debilitating ailment that has a profound impact on the quality of life of the patients. Fortunately, treatment for acne fulminans is straightforward. Systemic steroids are usually prescribed. A doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics if a patient develops acne fulminans.
An acute febrile disease accompanied by pain in the legs, arms, and hips, a 14-year-old male presents with painful lesions. He was also experiencing a low-grade fever. A radiograph of the affected extremities shows a small lytic area on the left fibula, soft-tissue swelling, and slight perlosteal necrosis. A patient with acne fulminans may be suffering from SAPHO syndrome, which includes bone lesions, constitutional symptoms, and laboratory abnormalities.
Although the onset of acne fulminans is often triggered by isotretinoin therapy, it may occur with or without isotretinoin therapy. In the case of acne fulminans induced by isotretinoin, treatment with corticosteroids is required. Steroids should be given for 4 weeks, whereas in cases without systemic involvement, steroids should be continued for a month or until the lesions are healed.
In severe cases, the disease can develop into a serious condition. Acne fulminans may include a fever and polyarthritis. It also causes inflammatory nodules on the trunk and palms of the affected extremities. Large nodules tend to form ulcers or exudative necrotic plaques, and erythematous neovascular lesions may also be present. Some patients may also complain of inflammatory arthralgia, synovitis, and osteomyelitis.
The lesions of acne fulminans may range in size from papules to pustules, to nodules and nodulocystic lesions. These lesions usually involve the face, neck, trunk, and back of the body, as well as the external auditory canals. Occasionally, patients develop acne conglobata and related follicular structures. When acne fulminans becomes severe, it can lead to scarring, sinus tract formation, and even arthralgia.




